| mysql> help |
| ? (\?) Synonym for `help'. |
| clear (\c) Clear the current input statement. |
| connect (\r) Reconnect to the server. Optional arguments are db and host. |
| delimiter (\d) Set statement delimiter. |
| edit (\e) Edit command with $EDITOR. |
| ego (\G) Send command to mysql server, display result vertically. |
| exit (\q) Exit mysql. Same as quit. |
| go (\g) Send command to mysql server. |
| help (\h) Display this help. |
| nopager (\n) Disable pager, print to stdout. |
| notee (\t) Don't write into outfile. |
| pager (\P) Set PAGER [to_pager]. Print the query results via PAGER. |
| print (\p) Print current command. |
| prompt (\R) Change your mysql prompt. |
| quit (\q) Quit mysql. |
| rehash (\#) Rebuild completion hash. |
| source (\.) Execute an SQL script file. Takes a file name as an argument. |
| status (\s) Get status information from the server. |
| system (\!) Execute a system shell command. |
| tee (\T) Set outfile [to_outfile]. Append everything into given outfile. |
| use (\u) Use another database. Takes database name as argument. |
| charset (\C) Switch to another charset. Might be needed for processing binlog with multi-byte charsets. |
| warnings (\W) Show warnings after every statement. |
| nowarning (\w) Don't show warnings after every statement. |
| resetconnection(\x) Clean session context. |
| |
| 常用 |
| \? 和'help'命令相同 |
| \c 阻止上个命令运行 |
| \G 格式化输出(逐行输出,针对列特别多的场景) |
| \q 退出会话(ctrl+d) |
| \. source 导入SQL脚本,类似于< |
| \! 调用linux命令 |
| linux当中一切皆命令,一切皆文件。 |
| mysql一切皆SQL,一切皆库、表。 |
数据定义语言
| create database 库名 charset utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_bin; |
| 数据库名 字符集 排序规则 |
| |
| 建库规范: |
| 1.库名不能有大写字母 #多平台兼容问题 |
| 2.建库要加字符集 |
| 3.库名不能有数字开头 |
| 4.库名要和业务相关 |
| 5.库名不要太长 |
| 6.不要使用内置字符 |
| |
| create database xiaowu; |
| show create database xiaowu; #查看建库的基本命令(建库语句) |
| show databases; |
| show create database xiaowu; #查看建库的基本命令(建库语句) |
| show create database school; |
| alter database xiaowu charset utf8; |
| |
| 注意:修改字符集,修改后的字符集一定是原字符集的严格超集 |
| 只能改库属性,不能改库名。 |
生产中谨慎使用
| mysql> drop database xiaowu; |
| create table stu( |
| 列1 属性(数据类型、约束、其他属性) , |
| 列2 属性, |
| 列3 属性 |
| ) |
| |
| USE school; |
| CREATE TABLE stu( |
| id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '学号', |
| sname VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '姓名', |
| sage TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '年龄', |
| sgender ENUM('m','f','n') NOT NULL DEFAULT 'n' COMMENT '性别' , |
| sfz CHAR(18) NOT NULL UNIQUE COMMENT '身份证', |
| intime TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT NOW() COMMENT '入学时间' |
| ) ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT '学生表'; |
| 列名 |
数据类型 |
长度 |
默认 |
主键 |
非空 |
无符号 |
自增 |
列值不重复 |
注释 |
| id |
int |
|
|
PRIMARY KEY |
NOT NULL |
|
AUTO_INCREMENT |
|
COMMENT ‘学号’ |
| name |
varchar |
255 |
|
|
NOT NULL |
|
|
|
COMMENT ‘姓名’ |
| age |
tinyint |
|
DEFAULT 0 |
|
NOT NULL |
UNSIGNED |
|
|
COMMENT ‘年龄’ |
| gender |
ENUM(‘m’,’f’,’n’) |
|
DEFAULT ‘n’ |
|
NOT NULL |
|
|
|
COMMENT ‘性别’ |
| sfz |
CHAR |
18 |
|
|
NOT NULL |
|
|
UNIQUE |
COMMENT ‘身份证’ |
| intinme |
TIMESTAMP |
|
DEFAULT NOW() |
|
NOT NULL |
|
|
|
COMMENT ‘入学时间’ |
| ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT '学生表' |
| 存储引擎 字符集 注释 |
建表规范:
| 1. 表名小写 |
| 2. 不能是数字开头 |
| 3. 注意字符集和存储引擎 |
| 4. 表名和业务有关 |
| 5. 选择合适的数据类型 |
| 6. 每个列都要有注释 |
| 7. 每个列设置为非空,无法保证非空,默认值或用0来填充。 |
| 8. 必须要有主键 |
| 9. 列名不要太长 |
练习:
| 1、表名过长 |
| 2、id bigint(20)过大 |
| 3、数字列应该用数字类型 |
| 4、distribution_cost应该使用小数 |
| 5、时间列应该datatime类型 |
| 6、is_deleted用枚举类型 |
| mysql> show tables; |
| mysql> desc wp_users; |
| mysql> show create table stu; |
例子:
| 1.在stu表中添加手机列 |
| ALTER TABLE stu ADD shouji bigint NOT NULL UNIQUE KEy COMMENT '手机号'; |
| |
| alter table stu add shouji bigint notnull unique key comment '手机号' first ; #列首添加 |
| |
| alter table stu add shouji bigint notnull unique key comment '手机号' after id ; #在id列后添加一个列 |
| |
| 2.手机列修改数据类型为char(11) modefy |
| alter table stu modify shouji char(11) not null unique key comment '手机号'; |
| alter table stu rename t2; 改表名 |
| 3.删除手机号列(危险操作) |
| mysql> alter table stu drop shouji; |
| mysql> drop table stu; |
| mysql> drop database 库名; |
| 1、创建一张表 |
| create table 库名.表名( |
| 列名 数据类型 约束 属性, |
| 列名 数据类型 约束 属性, |
| 列名 数据类型 约束 属性, |
| ... |
| )engine(引擎)=innodb charset(字符集)=utf8mb4; |
| |
| 2、线上DDL(alter)操作对于生产的影响 |
| 说明:在MySQL中,DDL语句在对表进行操作是,是要锁“元数据表”的。 |
| 扩展:元数据是什么? ---》类似linux inode信息 |
| 在MySQL中,DDL语句对表进行操作时,是要锁“元数据表”的,此时,所有修改类命令无法正常运行。所以在对于大表、业务繁忙的表,进行先上DDL操作时,要谨慎。尽量避开业务繁忙时间,进行DDL操作。 |
面试题回答要点:
| 1.SQL语句的意思是什么 |
| 以上四条语句是进行DDL加列操作 |
| 2.以上操作带来的影响 |
| 在MySQL中,DDL语句对表进行操作时,是要锁“元数据表”的,此时,所有修改类命令无法正常运行。所以在对于大表、业务繁忙的表,进行先上DDL操作时,要谨慎。尽量避开业务繁忙时间,进行DDL操作。 |
| 3.我们的建议: |
| (1)尽量避开业务繁忙时间,进行DDL。走流程 |
| (2)建议使用:pt-online-schema-change(pt-osc) gh-ost工具进行DDL操作,减少锁表影响 |
| (3)如果8.0版本,可以不适用pt工具,8.0之前需要借助以上工具 |
数据控制语言
| 8.0之前: |
| grant 权限 on 对象 to 用户 identified by '密码'; |
| grant 权限1,权限2,权限3... on 对象 to 用户 identified by '密码'; |
| 8.0之后: |
| create user 用户 identified by '密码'; |
| grant 权限 on 对象 to 用户; |
| grant 权限1,权限2,权限3... on 对象 to 用户; |
| ALL:SELECT,INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, DROP, RELOAD, SHUTDOWN, PROCESS, FILE, REFERENCES, INDEX, ALTER, SHOW DATABASES, SUPER, CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES, LOCK TABLES, EXECUTE, REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT, CREATE VIEW, SHOW VIEW, CREATE ROUTINE, ALTER ROUTINE, CREATE USER, EVENT, TRIGGER, CREATE TABLESPACE |
| ALL #以上所有权限,一般是管理员才拥有的 |
| 权限1,权限2,权限3... #普通用户 |
| grant option #超级管理员,给别的用户授权 |
| grant 权限1,权限2,权限3... on 对象 to 用户 with grant option; |
注意:不要随意授权grant option,不然该用户可以在服务器中为所欲为,包括删除自带的超级管理员(root@localhost)
| *.* |
| wordpress.* |
| wordpress.t1 |
| user #用户对mysql服务的权限 |
| db #用户对某个库的权限 |
| tables_priv #用户对某个表的权限 |
| columns_priv #用户对某列的权限 |
| |
| 查询所有用户对mysql服务的权限 |
| select * from mysql.user\G |
| |
| 查询所有用户对库的权限 |
| select * from mysql.db\G |
| |
| 查询所有用户对某个表的权限 |
| select * from mysql.tables_priv\G |
| |
| 查询所有用户对某列的权限 |
| select * from mysql.columns_priv\G |
需求1:创建管理员用户,windows机器的navicat登录到linux中的MySQL
| mysql> grant all on *.* to root@'10.0.0.%' identified by '123' with grant option; |
| |
| 查询创建的用户: |
| mysql> select user,host,authentication_string from mysql.user; |
| |
| 查询某个用户的权限: |
| mysql> show grants for root@'10.0.0.%'; |
| +--------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | Grants for root@10.0.0.% | |
| +--------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'10.0.0.%' WITH GRANT OPTION | |
| +--------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
| 查询所有用户对mysql服务的权限 |
| select * from mysql.user\G |
| |
| 查询所有用户对库的权限 |
| select * from mysql.db\G |
| |
| 查询所有用户对某个表的权限 |
| select * from mysql.tables_priv\G |
| |
| 查询所有用户对某列的权限 |
| select * from mysql.columns_priv\G |
需求2:创建一个应用用户app用户,能从windows上登录mysql,能够对app库下所有对象进行create,select,update,delete,insert操作
| mysql> grant create,update,select,insert,delete on app.* to app@'10.0.0.%' identified by '123'; |
| |
| mysql> show grants for app@'10.0.0.%'; |
| +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | Grants for app@10.0.0.% | |
| +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'app'@'10.0.0.%' | |
| | GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE ON `app`.* TO 'app'@'10.0.0.%' | |
| +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
| linux: |
| chmod -R 644 /data ----> chmod -R 755 /data |
| |
| MySQL: |
| MySQL中不能通过重复授权,修改权限,只能通过回收权限的方式进行修改 |
| |
| 回收'app'@'10.0.0.%'对app库的create权限 |
| revoke create on app.* from 'app'@'10.0.0.%'; |
| |
| 添加'app'@'10.0.0.%'对app库的create权限 |
| grant create on app.* to app@'10.0.0.%'; |
数据操作语言
作用:对表中的数据进行增、删、改
| --- 最标准的insert语句 |
| mysql> desc stu; #先看看有什么列 |
| mysql> insert into stu(id,sname,sage,sgender,sfz,intime) |
| -> values |
| -> (1,'zs',18,'m','123456',now()); |
| mysql> select * from stu; |
| +----+-------+------+---------+--------+---------------------+ |
| | id | sname | sage | sgender | sfz | intime | |
| +----+-------+------+---------+--------+---------------------+ |
| | 1 | zs | 18 | m | 123456 | 2021-02-28 15:27:03 | |
| +----+-------+------+---------+--------+---------------------+ |
| |
| --- 省事的写法 |
| mysql> insert into stu |
| -> values |
| -> (2,'ls',18,'m','1234567',now()); |
| mysql> select * from stu; |
| +----+-------+------+---------+---------+---------------------+ |
| | id | sname | sage | sgender | sfz | intime | |
| +----+-------+------+---------+---------+---------------------+ |
| | 1 | zs | 18 | m | 123456 | 2021-02-28 15:27:03 | |
| | 2 | ls | 18 | m | 1234567 | 2021-02-28 15:30:45 | |
| +----+-------+------+---------+---------+---------------------+ |
| |
| --- 针对性的录入数据 |
| mysql> insert into stu(sname,sfz) |
| -> values |
| -> ('w5','1233232'); |
| mysql> select * from stu; |
| +----+-------+------+---------+---------+---------------------+ |
| | id | sname | sage | sgender | sfz | intime | |
| +----+-------+------+---------+---------+---------------------+ |
| | 1 | zs | 18 | m | 123456 | 2021-02-28 15:27:03 | |
| | 2 | ls | 18 | m | 1234567 | 2021-02-28 15:30:45 | |
| | 3 | w5 | 0 | n | 1233232 | 2021-02-28 15:32:24 | |
| +----+-------+------+---------+---------+---------------------+ |
| |
| --- 同时录入多行数据 |
| mysql> insert into stu(sname,sfz) |
| -> values |
| -> ('ll','34314314'), |
| -> ('kk','3515315'), |
| -> ('jj','654364365'); |
| mysql> select * from stu; |
| +----+-------+------+---------+-----------+---------------------+ |
| | id | sname | sage | sgender | sfz | intime | |
| +----+-------+------+---------+-----------+---------------------+ |
| | 1 | zs | 18 | m | 123456 | 2021-02-28 15:27:03 | |
| | 2 | ls | 18 | m | 1234567 | 2021-02-28 15:30:45 | |
| | 3 | w5 | 0 | n | 1233232 | 2021-02-28 15:32:24 | |
| | 4 | ll | 0 | n | 34314314 | 2021-02-28 15:34:37 | |
| | 5 | kk | 0 | n | 3515315 | 2021-02-28 15:34:37 | |
| | 6 | jj | 0 | n | 654364365 | 2021-02-28 15:34:37 | |
| +----+-------+------+---------+-----------+---------------------+ |
| |
| insert into 库.表 select concat(user,"@",host) from mysql.user; |
| mysql> update stu set sname='zhaosi' where id=1; |
| |
| mysql> select * from stu; |
| +----+--------+------+---------+-----------+---------------------+ |
| | id | sname | sage | sgender | sfz | intime | |
| +----+--------+------+---------+-----------+---------------------+ |
| | 1 | zhaosi | 18 | m | 123456 | 2021-02-28 15:27:03 | |
| | 2 | ls | 18 | m | 1234567 | 2021-02-28 15:30:45 | |
| | 3 | w5 | 0 | n | 1233232 | 2021-02-28 15:32:24 | |
| | 4 | ll | 0 | n | 34314314 | 2021-02-28 15:34:37 | |
| | 5 | kk | 0 | n | 3515315 | 2021-02-28 15:34:37 | |
| | 6 | jj | 0 | n | 654364365 | 2021-02-28 15:34:37 | |
| +----+--------+------+---------+-----------+---------------------+ |
| |
| 注意:update语句必须要加where。 |
| mysql> delete from stu where id=6; |
| |
| mysql> select * from stu; |
| +----+--------+------+---------+----------+---------------------+ |
| | id | sname | sage | sgender | sfz | intime | |
| +----+--------+------+---------+----------+---------------------+ |
| | 1 | zhaosi | 18 | m | 123456 | 2021-02-28 15:27:03 | |
| | 2 | ls | 18 | m | 1234567 | 2021-02-28 15:30:45 | |
| | 3 | w5 | 0 | n | 1233232 | 2021-02-28 15:32:24 | |
| | 4 | ll | 0 | n | 34314314 | 2021-02-28 15:34:37 | |
| | 5 | kk | 0 | n | 3515315 | 2021-02-28 15:34:37 | |
| +----+--------+------+---------+----------+---------------------+ |
扩展
| 1、伪删除 |
| 用update来替代delete,最终保证业务中查不到(select)即可 |
| 删除id为1 |
| 原操作: |
| mysql> delete from stu where id=1; |
| |
| 伪删除: |
| 1.添加状态列 |
| ALTER TABLE stu ADD state TINYINT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1 ; |
| SELECT * FROM stu; |
| 2. UPDATE 替代 DELETE |
| UPDATE stu SET state=0 WHERE id=6; |
| 3. 业务语句查询 |
| SELECT * FROM stu WHERE state=1; |
| |
| 2、delete from stu ,drop table stu,truncate table stu的区别 |
| 1.都可以删除全表 |
| |
| 2.区别 |
| delete |
| 逻辑上,逐行删除。数据行多,操作慢 |
| 并没有真正从磁盘删除,只是在存储层面打标记,磁盘空间不立即释放。HWM高水位线()不会降低。(自增列继续) |
| |
| drop |
| 将表结构(元数据)和数据行物理层次删除 |
| |
| truncate |
| 清空表段中的所有数据页。物理层次删除全表数据磁盘空间立即释放,HWM高水位会降低。(自增列重新开始) |
| |
| |
| 可以 |
| 常规方法: |
| 都可以通过 备份+日志,恢复数据。 |
| |
| 灵活办法 |
| delete可以通过,翻转日志(binlog) |
| 三种删除数据情况,也可以通过《延时从库进行恢复》 |
数据查询语言
作用:获取表中的数据行
| 1.配合内置函数使用 |
| mysql> select now(); #查看当前时间 |
| mysql> select database(); #查看当前所在库 |
| mysql> select concat("hello word!"); #命令拼接,显示某字符串 |
| +-----------------------+ |
| | concat("hello word!") | |
| +-----------------------+ |
| | hello word! | |
| +-----------------------+ |
| mysql> select concat(user,"@",host) from mysql.user; |
| +-------------------------+ |
| | concat(user,"@",host) | |
| +-------------------------+ |
| | root@10.0.0.1 | |
| | mysql.session@localhost | |
| | mysql.sys@localhost | |
| | root@localhost | |
| +-------------------------+ |
| mysql> select user(); #查看当前登录用户 |
| |
| 2.计算 |
| mysql> select 10*100; #进行计算 |
| +--------+ |
| | 10*100 | |
| +--------+ |
| | 1000 | |
| +--------+ |
| |
| 3.查询数据库的参数 |
| mysql> select @@port; #查询当前端口 |
| mysql> select @@datadir; #查看数据存储位置 |
| |
| show variables; ##查看所有参数 |
| mysql> show variables like '%trx%'; #like 模糊查询 |
| 单表 |
| 前提: |
| select |
| 1.from 表1,表2,。。。 |
| 2.where 过滤条件1,过滤条件2... |
| 3.group by 条件列1 条件列2。。。分组字段 |
| 4.select_list 列名 |
| 5.having 过滤条件1 过滤条件2。。。 |
| 6.order by 条件列1 条件列2。。。排序字段 |
| 7.limit 分页限制 |
使用方法
准备学习环境[root@Centos7 ~]# mysql -p < world.sql 导入world库
| [root@Centos7 ~]# mysql -p < world.sql #导入world库 |
| world库常见单词 |
| world ===>世界 |
| city ===>城市 |
| country ===>国家 |
| countrylanguage ===>国家语言 |
| |
| city:城市表 |
| DESC city; |
| ID : 城市ID |
| NAME : 城市名 |
| CountryCode: 国家代码,比如中国CHN 美国USA |
| District : 省份 |
| Population : 人口数 |
| select配合from子句使用 |
| 语法: |
| select 列 from 表; |
| 例子: |
| #查询表中所有列所有行,*谨用! |
| select * from city; |
| #查询部分列值 |
| select name,population from city; |
| select+from+where配合使用 |
| where配合比较判断符=,<,>,>=,<=,!= |
| 例子: |
| #查询属于中国的所有城市信息 |
| mysql> select * from world.city where countrycode='CHN'; |
| #查询人口小于1000的所有城市信息 |
| mysql> select * from world.city where population < 1000; |
| select+from+where+like配合使用,模糊查询 |
| #查询city中,国家代号是CH开头的城市信息 |
| mysql> select * from world.city where countrycode like 'CH%'; |
| mysql> select * from world.city where countrycode like 'CH_'; |
| %:多个任意字符 |
| _:一个任意字符 |
| |
| 注:like语句在使用时,切记不要出现前面带%的模糊查询,原因:不走索引。 |
| #只要前面有%的模糊查询,就不会走索引 |
| select * from world.city where countrycode like '%CH%'; |
| select+from+where+逻辑连接符(and or) |
| #例子:查询中国城市人口超过500W的城市 |
| mysql> select * from world.city |
| -> where countrycode='CHN' and population>5000000; |
| |
| #查询中国或美国的城市信息 |
| mysql> select * from world.city where countrycode='CHN' or countrycode='USA'; |
| |
| #查询中国和美国的信息,并且人口数量超过500W的城市; |
| mysql> select * from world.city where countrycode in ('CHN','USA') and population>5000000; |
| where配合between and |
| #作用:查询数值的一个范围 |
| #查询人口在100W和两百万之前的城市信息 |
| mysql> select * from world.city where population between 1000000 and 2000000; |
| mysql> select * from world.city where population>=1000000 and population<=2000000; |
| #作用:对一张表,按照不同数据特点,需要分组计算统计是,会使用group by+聚合函数 |
| group by 配合聚合函数(max(),min(),avg(),count(),sum(),group_concat())使用 |
| 聚合函数: |
| max() #最大值 |
| min() #最小值 |
| avg() #平均值 |
| count() #统计个数 |
| sum() #求和 |
| group_concat() #列转行 |
| |
| #说明:碰到group_by必然会有聚合函数 |
| |
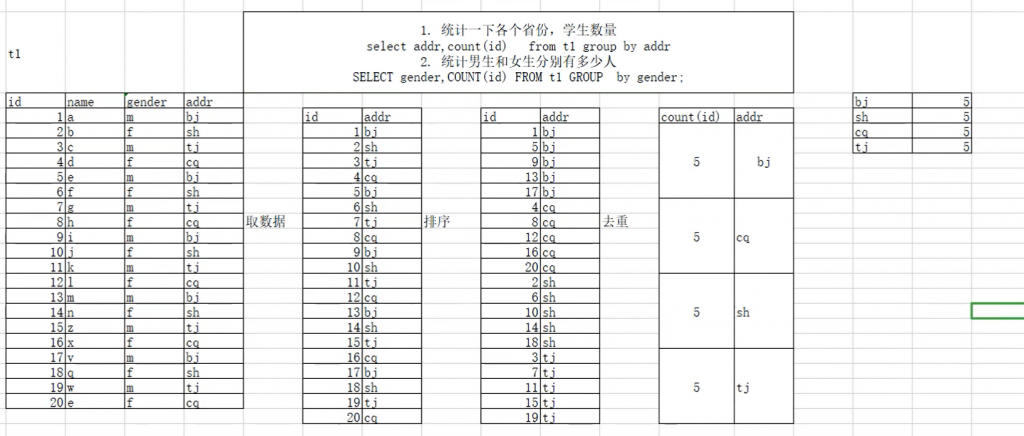
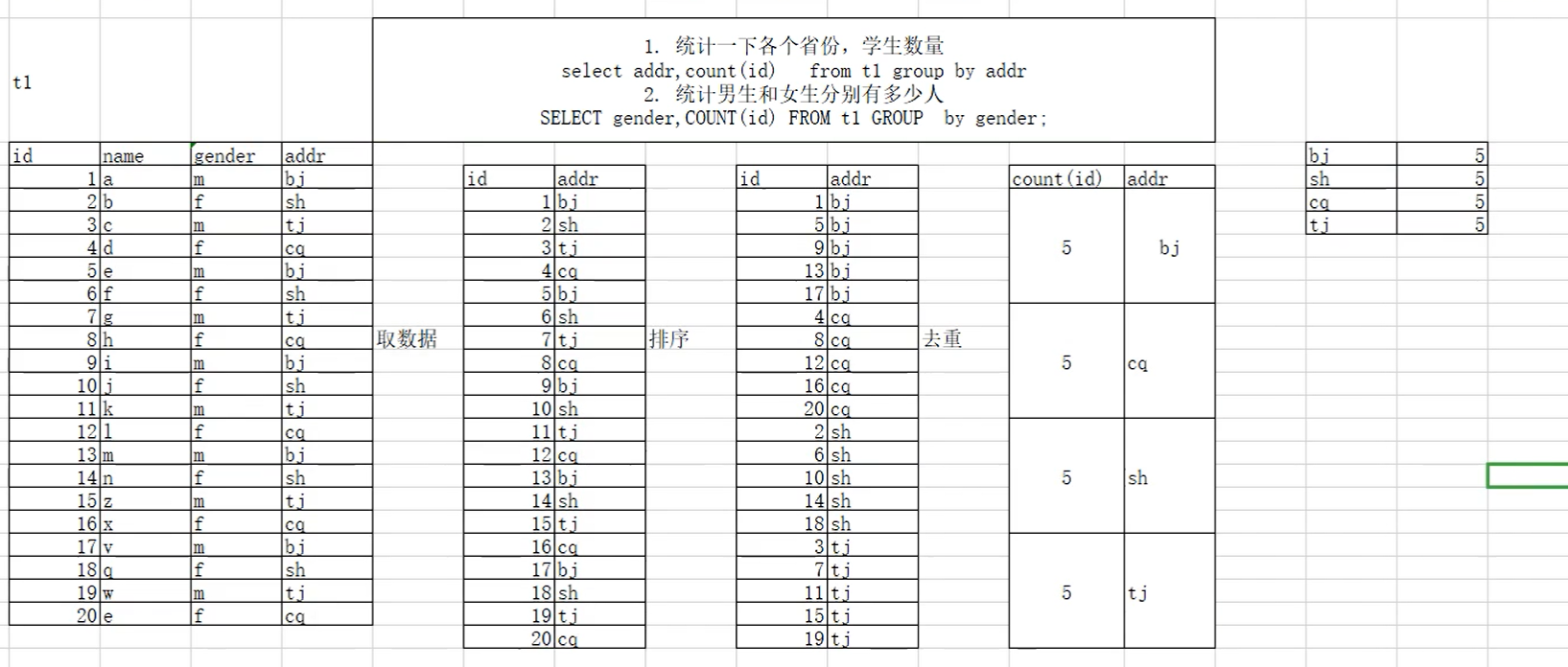
| 运行过程: |
| 提取数据--》排序--》去重--》统计 |
| # 统计city中,每个国家的城市个数 |
| select countrycode,count(id) from world.city group by countrycode; |
| |
| # 统计中国每个省的城市个数 |
| mysql> select district,count(id) from world.city where countrycode='CHN' group by district; |
| |
| #统计每个国家的总人口 |
| mysql> select countrycode,sum(population) from world.city group by countrycode; |
| |
| #统计中国,每个省的总人口 |
| mysql> select district,sum(population) from world.city where countrycode='CHN' group by district; |
| |
| #统计中国,每个省总人口,城市个数,城市名列表 |
| mysql> select district,sum(population),count(id),group_concat(name) from world.city where countrycode='CHN' group by district; |
| #作用:与where作用相似,都是过滤作用,但having是后过滤 where|group by|having |
| |
| #统计中国,每个省的总人口,只打印总人口数大于500W |
| mysql> select district,sum(population) from world.city where countrycode='CHN' group by district having sum(population)>5000000; |
| #作用:从小到大排序 默认由小到大添加desc后变成又大到小 |
| #统计中国,每个省的总人口,只打印总人口数大于500W,并且按照总人口从大到小排序输出 |
| select district,sum(population) from world.city where countrycode='CHN' group by district having sum(population)>5000000 order by sum(population) desc; |
| |
| 默认升序:asc |
| 降序:desc |
| #作用:分页输出 |
| #统计中国,每个省的总人口,只打印总人口数大于500W,并且按照总人口从大到小排序输出,只看前五名 |
| mysql> select district,sum(population) from world.city where countrycode='CHN' group by district having sum(population)>5000000 order by sum(population) desc limit 5; |
| |
| #统计中国,每个省的总人口,只打印总人口数大于500W,并且按照总人口从大到小排序输出,看6到10名 |
| mysql> select district,sum(population) from world.city where countrycode='CHN' group by district having sum(population)>5000000 order by sum(population) desc limit 5,5; |
| mysql> select district,sum(population) from world.city where countrycode='CHN' group by district having sum(population)>5000000 order by sum(population) desc limit 5 offset 5; |
| |
| ##统计中国,每个省的总人口,只打印总人口数大于500W,并且按照总人口从大到小排序输出,看3到5名 |
| mysql> select district,sum(population) from world.city where countrycode='CHN' group by district having sum(population)>5000000 order by sum(population) desc limit 2,3; |
| |
| mysql> select district,sum(population) from world.city where countrycode='CHN' group by district having sum(population)>5000000 order by sum(population) desc limit 3 offset 2; |
| #去重复 |
| mysql> select countrycode from world.city; |
| mysql> select distinct(countrycode) from world.city; |
| #查询中国或美国的城市信息 |
| mysql> select * from world.city where countrycode in ('CHN','USA'); |
| |
| mysql> select * from world.city where countrycode='CHN' union all select * from world.city where countrycode='USA'; |
| #先查中国的再查美国的。 |
| |
| 说明:一般情况下,我们会将 IN 或者 OR 语句 改写成 UNION ALL,来提高性能 |
| UNION 聚合两个结果集,会自动去重复 |
| UNION ALL 聚合两个结果集,不去重复 |
按需求创建一下表结构
| use school |
| student :学生表 |
| sno: 学号 |
| sname:学生姓名 |
| sage: 学生年龄 |
| ssex: 学生性别 |
| |
| teacher :教师表 |
| tno: 教师编号 |
| tname:教师名字 |
| |
| course :课程表 |
| cno: 课程编号 |
| cname:课程名字 |
| tno: 教师编号 |
| |
| score :成绩表 |
| sno: 学号 |
| cno: 课程编号 |
| score:成绩 |
| |
| -- 项目构建 |
| drop database school; |
| CREATE DATABASE school CHARSET utf8mb4; |
| USE school |
| |
| CREATE TABLE student( |
| sno INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '学号', |
| sname VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '姓名', |
| sage TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL COMMENT '年龄', |
| ssex ENUM('f','m') NOT NULL DEFAULT 'm' COMMENT '性别' |
| )ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET=utf8; |
| |
| CREATE TABLE course( |
| cno INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY COMMENT '课程编号', |
| cname VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '课程名字', |
| tno INT NOT NULL COMMENT '教师编号' |
| )ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET utf8; |
| |
| alter TABLE sc ( |
| sno INT NOT NULL COMMENT '学号', |
| cno INT NOT NULL COMMENT '课程编号', |
| score INT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '成绩' |
| )ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET=utf8; |
| |
| CREATE TABLE teacher( |
| tno INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY COMMENT '教师编号', |
| tname VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '教师名字' |
| )ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET utf8; |
| |
| INSERT INTO student(sno,sname,sage,ssex) |
| VALUES (1,'zhang3',18,'m'); |
| |
| INSERT INTO student(sno,sname,sage,ssex) |
| VALUES |
| (2,'zhang4',18,'m'), |
| (3,'li4',18,'m'), |
| (4,'wang5',19,'f'); |
| |
| INSERT INTO student |
| VALUES |
| (5,'zh4',18,'m'), |
| (6,'zhao4',18,'m'), |
| (7,'ma6',19,'f'); |
| |
| INSERT INTO student(sname,sage,ssex) |
| VALUES |
| ('oldboy',20,'m'), |
| ('oldgirl',20,'f'), |
| ('oldp',25,'m'); |
| |
| INSERT INTO teacher(tno,tname) VALUES |
| (101,'oldboy'), |
| (102,'hesw'), |
| (103,'oldguo'); |
| |
| DESC course; |
| INSERT INTO course(cno,cname,tno) |
| VALUES |
| (1001,'linux',101), |
| (1002,'python',102), |
| (1003,'mysql',103); |
| |
| DESC sc; |
| INSERT INTO sc(sno,cno,score) |
| VALUES |
| (1,1001,80), |
| (1,1002,59), |
| (2,1002,90), |
| (2,1003,100), |
| (3,1001,99), |
| (3,1003,40), |
| (4,1001,79), |
| (4,1002,61), |
| (4,1003,99), |
| (5,1003,40), |
| (6,1001,89), |
| (6,1003,77), |
| (7,1001,67), |
| (7,1003,82), |
| (8,1001,70), |
| (9,1003,80), |
| (10,1003,96); |
| |
| SELECT * FROM student; |
| SELECT * FROM teacher; |
| SELECT * FROM course; |
| SELECT * FROM sc; |
将多张表合成一张大表
查询张三的家庭住址
| SELECT A.name,B.address FROM |
| A JOIN B |
| ON A.id=B.id |
| WHERE A.name='zhangsan' |
| 1、为什么要使用多表连接查询? |
| 我们的查询需求,需要的数据,来自于多张表,单张表无法满足。 |
| 2、简单理解: |
| 多表连接实际上是将多张表中,有关联的部分数据,合并成一张新表,在新表中去做 where、group、having、order by、limit |
1.笛卡尔乘积(不常见)
| mysql> select * from teacher,course; |
| +-----+--------+------+--------+-----+ |
| | tno | tname | cno | cname | tno | |
| +-----+--------+------+--------+-----+ |
| | 101 | oldboy | 1001 | linux | 101 | |
| | 102 | hesw | 1001 | linux | 101 | |
| | 103 | oldguo | 1001 | linux | 101 | |
| | 101 | oldboy | 1002 | python | 102 | |
| | 102 | hesw | 1002 | python | 102 | |
| | 103 | oldguo | 1002 | python | 102 | |
| | 101 | oldboy | 1003 | mysql | 103 | |
| | 102 | hesw | 1003 | mysql | 103 | |
| | 103 | oldguo | 1003 | mysql | 103 | |
| +-----+--------+------+--------+-----+ |
| 9 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
| |
| mysql> select * from teacher join course; |
| +-----+--------+------+--------+-----+ |
| | tno | tname | cno | cname | tno | |
| +-----+--------+------+--------+-----+ |
| | 101 | oldboy | 1001 | linux | 101 | |
| | 102 | hesw | 1001 | linux | 101 | |
| | 103 | oldguo | 1001 | linux | 101 | |
| | 101 | oldboy | 1002 | python | 102 | |
| | 102 | hesw | 1002 | python | 102 | |
| | 103 | oldguo | 1002 | python | 102 | |
| | 101 | oldboy | 1003 | mysql | 103 | |
| | 102 | hesw | 1003 | mysql | 103 | |
| | 103 | oldguo | 1003 | mysql | 103 | |
| +-----+--------+------+--------+-----+ |
| 9 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
2.内连接(应用最广泛)
| select 列名。。。 |
| from A join B |
| on A.xx=B.yy |
| mysql> select * from teacher join course on teacher.tno=course.tno; |
| +-----+--------+------+--------+-----+ |
| | tno | tname | cno | cname | tno | |
| +-----+--------+------+--------+-----+ |
| | 101 | oldboy | 1001 | linux | 101 | |
| | 102 | hesw | 1002 | python | 102 | |
| | 103 | oldguo | 1003 | mysql | 103 | |
| +-----+--------+------+--------+-----+ |
3.外连接
| #作用:强制驱动表 |
| 驱动表:在多表连接中,承当for循环中外层循环的角色,此时,MySQL会拿着驱动表的每个满足条件的关联列的值,去一次找到for循环内循环中的关联值一一进行判断和匹配。(next loop)。 |
| 建议:将结果集小的表设置为驱动表更加合适,可以降低next loop的次数。对于内连接来讲,我们是没法控制驱动表是谁,完全由优化器决定。如果需要人为干预,需要将内连接写成外连接的方式。 |
| |
| 1、left join #左边的所有的数据列都要取到,右表满足条件的数据,强制左表为驱动表 |
| mysql> select city.name,country.name,city.population from city left join country on city.countrycode = country.code and city.population<100 order by city.population desc; |
| |
| 2、right join #右边的所有的数据列都要取到,左表满足条件的数据,强制右表为驱动表 |
| mysql> select city.name,country.name,city.population from city right join country on city.countrycode = country.code and city.population<100; |
| mysql> select city.name,country.name,city.population from city left join country on city.countrycode = country.code and city.population<100 order by city.population desc |
| union |
| mysql> select city.name,country.name,city.population from city right join country on city.countrycode = country.code and city.population<100; |
例子一:查询wuhan这个城市,国家名、城市名、城市人口数、国土面积。
| 1、找关联表: |
| city: |
| 城市名(city.name) |
| 城市人口(city.population) |
| country: |
| 国家名(country.name) |
| 国土面积(country.surfacearea) |
| from city join country |
| |
| 2、找关联条件 |
| mysql> desc city; |
| mysql> desc country; |
| #发现city.countrycode和country.code有关联 |
| from city join country on city.countrycode=country.code |
| |
| 3、罗列其他查询条件 |
| mysql> |
| select city.name, |
| city.population, |
| country.name, |
| country.surfacearea |
| from city |
| join country |
| on city.countrycode=country.code |
| where city.name='wuhan'; |
例子二:统计学员zhang3,学习了几门课
| 1、找关联表 |
| student.sname |
| count(sc.cno) |
| from student join sc |
| 2、找关联条件 |
| from student join sc |
| on student.sno=sc.sno |
| 3、罗列其他条件 |
| mysql> select student.sno as 学号, |
| student.sname as 学生姓名, |
| count(sc.cno) as 学习课数 |
| from sc |
| join student |
| on sc.sno=student.sno |
| where student.sname='zhang3' |
| group by student.sno; |
| +--------+--------------+--------------+ |
| | 学号 | 学生姓名 | 学习课数 | |
| +--------+--------------+--------------+ |
| | 1 | zhang3 | 2 | |
| +--------+--------------+--------------+ |
例子三:查询zhang3,学习的课程名称有哪些
| 1、找关联表 |
| student.sname |
| sc.sno,sc.cno |
| course.cname |
| 2、找关联条件 |
| student.sname |
| sc.sno,sc.cno |
| course.cname |
| from student |
| join sc |
| on student.sno = sc.sno |
| join course |
| on sc.cno = course.cno |
| 3、罗列条件 |
| mysql> select student.sno as 学号, |
| student.sname as 学生姓名, |
| group_concat(course.cname) as 课程名称 |
| from student |
| join sc |
| on student.sno=sc.sno |
| join course |
| on sc.cno=course.cno |
| where student.sname='zhang3' |
| group by student.sno; |
| +--------+--------------+--------------+ |
| | 学号 | 学生姓名 | 课程名称 | |
| +--------+--------------+--------------+ |
| | 1 | zhang3 | python,linux | |
| +--------+--------------+--------------+ |
例子四:查询oldguo老师教的学生名
| 1、找关联条件、关联表 |
| select teacher.tname,student.sname |
| on teacher.tno = course.tno |
| on course.cno = sc.cno |
| on sc.sno = student.sno |
| 2、罗列条件 |
| select teacher.tname, |
| group_concat(student.sname) |
| from teacher |
| join course |
| on teacher.tno = course.tno |
| join sc |
| on course.cno = sc.cno |
| join student |
| on sc.sno = student.sno |
| where teacher.tname='oldguo'; |
例子五:查询oldguo所教课程的平均分数
| select teacher.tname,avg(sc.score) |
| from teacher |
| join course |
| on teacher.tno = course.tno |
| join sc |
| on course.cno = sc.cno |
| where teacher.tname='oldguo'; |
例子六:每位老师所教课程的平均分,并按平均分排序
| mysql> select teacher.tname, |
| avg(sc.score) |
| from teacher |
| join course |
| on teacher.tno = course.tno |
| join sc |
| on course.cno = sc.cno |
| group by teacher.tname |
| order by avg(sc.score) |
| desc; |
| +--------+---------------+ |
| | tname | avg(sc.score) | |
| +--------+---------------+ |
| | oldboy | 80.6667 | |
| | oldguo | 76.7500 | |
| | hesw | 70.0000 | |
| +--------+---------------+ |
例子七:查询oldguo所教的不及格的学生姓名
| mysql> select teacher.tname, |
| student.sname, |
| sc.score |
| from teacher |
| join course |
| on teacher.tno = course.tno |
| join sc |
| on course.cno = sc.cno |
| join student |
| on sc.sno = student.sno |
| where teacher.tname='oldguo' |
| and sc.score < 60; |
| +--------+-------+-------+ |
| | tname | sname | score | |
| +--------+-------+-------+ |
| | oldguo | li4 | 40 | |
| | oldguo | zh4 | 40 | |
| +--------+-------+-------+ |
例子八:查询所有老师所教学生不及格的信息
| mysql> select teacher.tname, student.sname, sc.score from teacher join course on teacher.tno = course.tno join sc on course.cno = sc.cno join student on sc.sno = student.sno where sc.score < 60; |
| +--------+--------+-------+ |
| | tname | sname | score | |
| +--------+--------+-------+ |
| | hesw | zhang3 | 59 | |
| | oldguo | li4 | 40 | |
| | oldguo | zh4 | 40 | |
| +--------+--------+-------+ |
例子九:查询平均成绩大于60分的同学的学号和平均成绩
| select student.sno, |
| student.sname, |
| avg(sc.score) |
| from student |
| join sc |
| on student.sno=sc.sno |
| group by student.sno |
| having avg(sc.score)>60; |
例子十:查询所有同学的学号、姓名、选课数、总成绩、平均成绩
| select student.sno, |
| student.sname, |
| count(*), |
| sum(sc.score), |
| avg(sc.score) |
| from student |
| join sc |
| on student.sno = sc.sno |
| group by student.sno; |
例子十一:查询各科成绩的最高分和最低分:以如下形式显示:课程ID,最高分,最低分***
| select sc.cno as 课程id, |
| max(sc.score) as 最高分, |
| min(sc.score) as 最低分 |
| from sc |
| group by sc.cno; |
例子十二:统计各位老师,所教课程的及格率(及格人数/总人数)***
| ##case语法 |
| case when 判断 then 结果 end |
| |
| # |
| select teacher.tname as 教师姓名, |
| concat(count(case when sc.score>60 then 1 end)/count(*)*100,"%") as 及格率 |
| from teacher |
| join course |
| on teacher.tno = course.tno |
| join sc |
| on course.cno = sc.cno |
| group by teacher.tno; |
例子十三:查询出只选修了一门课程的全部学生的学号和姓名
| select student.sno ,student.sname,count(*) |
| from student |
| join sc |
| on student.sno = sc.sno |
| group by student.sno |
| having count(*) = 1; |
例子十五:查询选修课程门数超过1门的学生信息
| select student.sno ,student.sname,count(*) |
| from student |
| join sc |
| on student.sno = sc.sno |
| group by student.sno |
| having count(*) > 1; |
例子十六:统计每门课程优秀(85分以上),良好(70-85),一般(60-70),不及格(小于60)的学生列表***
| select course.cname, |
| group_concat( |
| case when sc.score>=85 |
| then student.sname |
| end) as 优秀, |
| group_concat( |
| case when sc.score>=70 |
| and sc.score<85 |
| then student.sname |
| end) as 良好, |
| group_concat( |
| case when sc.score>=60 |
| and sc.score<70 |
| then student.sname |
| end) as 一般, |
| group_concat( |
| case when sc.score<60 |
| then student.sname |
| end) as 不及格 |
| from student |
| join sc |
| on student.sno=sc.sno |
| join course |
| on sc.cno=course.cno |
| group by course.cno; |
例子十七:查询平均成绩大于85的所有学生的学号、姓名和平均成绩
| select student.sno, |
| student.sname, |
| avg(sc.score) |
| from student |
| join sc |
| on student.sno=sc.sno |
| group by student.sno |
| having avg(sc.score)>85; |
| #别名是一次性的名字,仅限当前select使用。但可以在全局调用定义的别名 |
| 列别名,表别名 |
| SELECT |
| a.Name AS an , |
| b.name AS bn , |
| b.SurfaceArea AS bs, |
| a.Population AS bp |
| FROM city AS a JOIN country AS b |
| ON a.CountryCode=b.Code |
| WHERE a.name ='shenyang'; |
| |
| mysql> select city.name,city.population,country.name,country.surfacearea from city join country on city.countrycode=country.code where city.name='wuhan'; |
| +-------+------------+-------+-------------+ |
| | name | population | name | surfacearea | |
| +-------+------------+-------+-------------+ |
| | Wuhan | 4344600 | China | 9572900.00 | |
| +-------+------------+-------+-------------+ |
| |
| mysql> select city.name as 城市名,city.population as 城市人口,country.name as 国家名,country.surfacearea as 国土面积 from city join country on city.countrycode=country.code where city.name='wuhan'; |
| +-----------+--------------+-----------+--------------+ |
| | 城市名 | 城市人口 | 国家名 | 国土面积 | |
| +-----------+--------------+-----------+--------------+ |
| | Wuhan | 4344600 | China | 9572900.00 | |
| +-----------+--------------+-----------+--------------+ |
| show databases; #查看所有数据库 |
| show tables; #查看当前库的所有表 |
| SHOW tables from #查看某个指定库下的表 |
| show create database world #查看建库语句 |
| show create table world.city #查看建表语句 |
| show grants for root@'localhost' #查看用户的权限信息 |
| show charset; #查看字符集 |
| show collation #查看校对规则 |
| show processlist; #查看数据库连接情况 |
| show full processlist; #查看数据库连接情况,且显示info的详细信息 |
| show privileges #查看支持的权限信息 |
| show index from #表的索引情况 |
| show status #数据库状态查看 |
| SHOW STATUS LIKE '%lock%'; #模糊查询数据库某些状态 |
| SHOW variables #查看所有配置信息 |
| SHOW variables LIKE '%lock%'; #模糊查看部分配置信息 |
| show engines #查看支持的所有的存储引擎 |
| show engine innodb status\G #查看InnoDB引擎相关的状态信息 |
| show binary logs #列举所有的二进制日志 |
| show master status #查看数据库的日志位置信息 |
| show binlog evnets #查看二进制日志事件 |
| show master status; #查询二进制日志的位置点信息 |
| show slave status\G #查看从库状态 |
| SHOW RELAYLOG EVENTS in #查看从库relaylog事件信息,查看中继日志事件 |
| desc (show colums from city) #查看表的列定义信息 |
| |
| http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/show.html |